Hola and welcome to a new grammar lesson. This time, we will discuss the rules to use direct object pronouns in Spanish, a special type of pronouns used to refer to things and people. They are essential in daily conversations, as they help to simplify speech and let the other person know who or what we are talking about. Let’s start…
What are direct object pronouns in Spanish?
Direct object pronouns in Spanish are words like “LO, LOS, LA, LAS, LE” that are always used to refer to an object that had been mentioned before in a conversation. As we will soon see in this lesson, the pronoun to use in a sentence must correspond with the number and gender of the objects we refer to. Let’s take a look at this sentence:
- “El televisor está encendido“, (The TV is on.)
Here, the words “el televisor” (the TV) are the main object in this sentence. If we ask ourselves, “¿Qué es lo que está encendido?” (What’s on?), the answer is “el televisor”, that is, the direct object of this sentence. Since “TELEVISOR” is a singular, masculine noun, we should add a pronoun that matches its gender and number such as “LO”, just like this:
- “El televisor está encendido”, ¿Quién lo encendió? (The TV is on. Who turned it on?)
On the other hand, for a singular feminine noun like BILLETERA (wallet), we must use LA: “Busqué la billetera media hora, pero al fin la encontré” (I found it).
Here is a chart for Spanish direct object pronouns, plus a few examples similar to the ones we will see later.
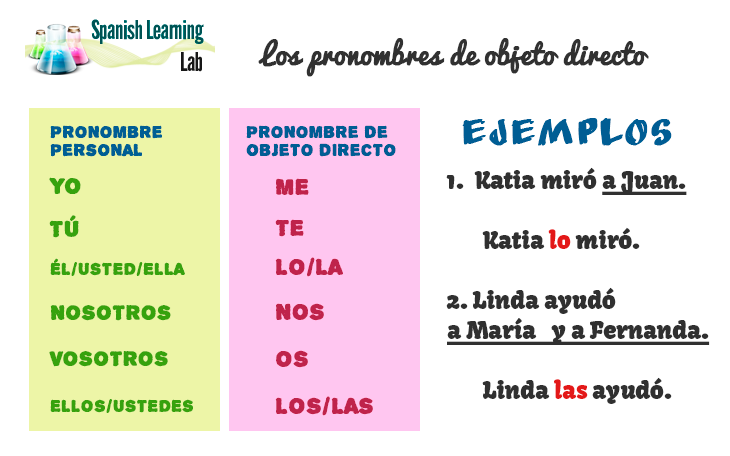
How to use direct object pronouns in Spanish to refer to people
Let’s try to understand where direct object pronouns, “los pronombres de objeto directo“, come from. Direct object pronouns will only replace people’s names when the preposition “A” is used to show some kind of relationship between a subject and an object, just the way “TO” is used in the English language sometimes. For instance, a sentence like “Ana listens to Carlos”, where “Ana” is the subject and “Carlos” is the object, would be easily translated into “Ana escucha a Carlos”. The word “A” corresponds to the preposition TO in this case. Other sentences following this pattern are:
- Pedro mira a María. (Pedro looks at Maria)
- El maestro ayudó a Carlos y María (The teacher helped Carlos and María)
In order to use a direct object pronouns in Spanish for the first sentence, we must replace the noun “Carlos” with a pronoun in singular, masculine form such as “LO” or the neuter pronoun “LE”. After identifying the object pronoun that we need, we must place it before the correct conjugation of the verb (ESCUCHA), having “Ana lo escucha” as a result of the transformation. The same process can be used for the other two examples:
- Pedro la mira. (Pedro looks at her)
- El maestro los ayudó. (The teacher helps them)
Sometimes, people will substitute the pronoun LO for LE, something called “leísmo”. This way, we could have also said: “Ana le escucha.” (Ana listens to him). Check the examples in the picture below for more details:

Following the same rule, it is all a matter of finding the right pronoun to replace the object in the sentence for one of the pronouns in the chart. Please listen and analyze the following group of sentences using direct object pronouns in Spanish to refer to people.
| Examples using Spanish direct object pronouns |
|---|
|
Carmen ayuda a María / Carmen la ayuda / Carmen le ayuda
Carmen helps María / Carmen helps her
|
|
Fernando cuida a los niños / Fernando los cuida / Fernando les cuida.
Fernando takes care of the children/ Fernando takes care of them
|
| El guía ayudó a Juan / El guía lo ayudó/ El guía le ayudó. The guide helped Juan / The guide helped him |
How to use direct object pronouns in Spanish for things
If you understood how to use these pronouns to replace people when they work as the object of the sentence, then it will be a lot easier for things. A sentence like “Carlos bought a car” can be translated into “Carlos compró un auto”. The main object in this sentence is “un auto”, something we know by asking ourselves the question “¿Qué es lo que + action in the sentence?” as in ¿Qué es lo que Carlos compró? – Un auto. Now that we know what the object is, we can replace this noun for a pronoun that matches it in gender and number, that is “LO”. With that in mind, we can simply say “Carlos lo compró” where LO refers to the car itself. Here is a picture illustrating this relationship between objects and these pronouns a bit better:
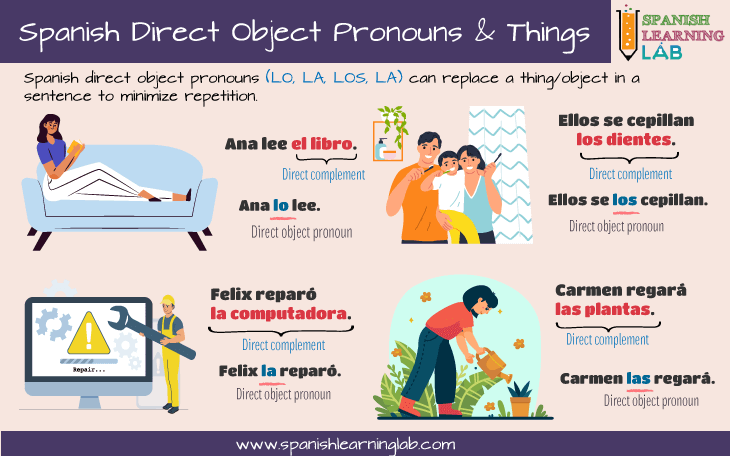
Next, read and listen to some examples of sentences using object pronouns in Spanish to replace things:
| Examples using Spanish direct object pronouns |
|---|
|
Maria perdió su muñeca / María la perdió.
Maria lost her doll / Maria lost it(the doll)
|
|
Los estudiantes compraron los libros / Los estudiantes los compraron.
The students bought the books / The students bought them
|
|
El bebé abrió el bote / El bebé lo abrió
The baby opened the jar / The baby opened it
|
As you can see in the example, we need to be careful to use the appropriate Spanish direct object pronoun for the object we are referring to. SE is a special pronoun, often used in an impersonal way meaning BY ITSELF like in the sentences “La película se terminó” (The movie is over). Here are some more examples:
| Examples with Spanish direct object pronouns |
|---|
|
El televisor está encendido. ¿Lo puedes apagar?
The TV is on. Can you turn it off?
|
| Yo perdí mi billetera, pero la encontré después I lost my wallet, but I found it later. |
|
¿Viste los juguetes? No los encontramos
Did you see the toys? We couldn’t find them
|
|
Tengo las llaves. Las encontré en la cocina
I have the keys. I found them in the kitchen.
|
|
El carro se dañó.
The car broke down
|
Related PDF Worksheets:
- Subject Pronouns in Spanish
- Basic Sentence Structure in Spanish
- Direct Object Pronouns in Spanish
- Indirect Object Pronouns in Spanish
